RFID is a non-contact automatic identification technology. With the continuous development of wireless network technology, RFID technology has been widely used at home and abroad. Now the development of smart earth and China's Internet of Things technology proposed by IBM has greatly promoted the RFID function. Therefore, RFID technology bridges the gap between the digital world and the physical world, laying the foundation for the development of the Internet of Things. Although RFID has been greatly developed, there are still some problems such as transmission distance and anti-collision algorithm for remote RFID. This paper analyzes the related concepts and technologies of RFID, so that people can more fully understand RFID and promote the development and application of RFID technology.
1 Remote RFID principle
1.1 The composition of remote RFID
Before discussing the principles of remote RFID, we must first study the composition of RFID. The RFID system consists of three parts: an electronic tag (TAG), a reader (Reader), and a computer and its application software. The electronic tag is mainly composed of a built-in antenna and a circuit chip, and the function is to complete communication with the radio frequency antenna; the reader/writer is mainly composed of an antenna, a control unit, a front-end section of the radio frequency transceiver, and a communication interface, and the main function is to read Or the information written to the electronic tag; the function of the computer and the application software is to connect the computer of the external meter through the communication interface of the reader/writer, or to connect to the host computer main system, thereby realizing data exchange. The RFID system is composed.
1.2 How Remote RFID Works
The reader and the electronic tag (TAG) form a transponder, which works. The Reader transmits a specific frequency of radio wave energy to the Transponder to drive the Transponder circuit to send the internal data. At this time, the Reader sequentially receives the interpreted data and sends it to the application for corresponding processing. The working principle is shown in Figure 2.
2 characteristics of remote RFID system
Currently, passive long-range remote RFID systems have two operating bands UHF and 2.45 GHz. The passive UHF system can read and write distances of up to ten meters or more, which is much farther than the 2.45 GHz system, so it has become the mainstream part of the remote identification system. The main advantages are as follows:
1) Real-time: It can respond in real time, automatically read the ID number and get its information;
2) Anti-counterfeiting: The formed microwave marks are unforgeable, altered and non-reproducible;
3) Networking: monitoring the logistics through the computer network;
4) Accuracy: The accuracy of reading information is very high and can be as high as 99.99%;
5) Low cost: only a few yuan is needed when using it;
6) Reliability: Adapt to harsh environmental conditions, such as: dusty, humid, etc.;
7) Long life: no battery is required for use, only passive card is required, and maintenance is free for life;
Since the remote RFID system adopts the wireless transmission mode and the wireless environment is extremely complicated, there are many factors that affect the read/write distance of the remote RFID system, mainly in the following aspects:
1) The factors affecting the reading and writing distance of the RF card are the RF output power of the reader, the reflected energy and the power consumption of the RF card, the received energy and the receiving sensitivity of the reader;
2) The above indicators are affected by the effective receiving and reflecting cross-sectional area of ​​the RF card antenna and the effective area of ​​the receiving antenna of the reader/writer;
3) Under the same conditions of the field of view, when the frequency increases, the range of the passive RFID system will decrease.
3 Remote RFID key technology
A wireless transmission method used by a remote RFID system is transmitted and received by electromagnetic waves when transmitting information. The electromagnetic wave is centered on the antenna and is emitted to the surrounding space. When the electromagnetic wave encounters different targets during the launch, part of the electromagnetic wave energy is absorbed by the target, and the other part is scattered in various directions with different intensities. A portion of the reflected energy eventually returns to the transmitting antenna. Energy transfer using backscatter modulation primarily signals both the energy transfer to the reader and the energy transfer from the reader to the tag.
1) Reader to tag energy transfer
The power density at the electronic tag at a distance R from the reader is given by equation (1):
Where, PTX is the transmit power of the reader, GTX is the gain of the transmit antenna, R is the distance between the tag and the antenna of the reader, and EIRP is the effective radiated power of the antenna, which refers to the transmit power and antenna gain of the reader. The product of.
When the state of the electronic tag and the transmitting antenna is optimal and the polarization direction is matched, the maximum power absorbed by the electronic tag is proportional to the density S of the power of the signal transmitted by the reader, as in equation (2):
1.5 inch / 125 mm Medium Duty Caster Wheel PVC/ PU / TPR
2.High quality galvanized support
3.Single wheel PVC / PU / TPR / PVC material
4.Double ball bearings
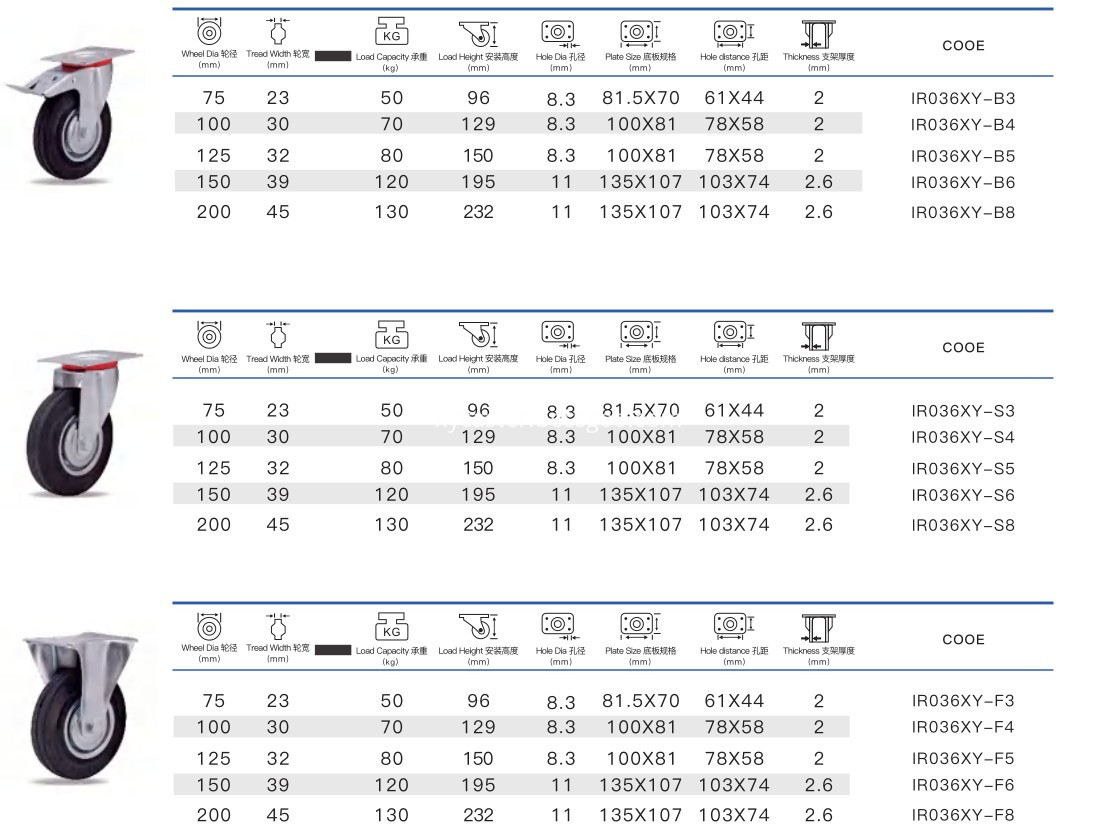
Swivel Wheels,5 Inch Medium Duty Casters,5 Inch Medium Duty Caster Wheels,5 Inch Swivel Wheels
Yangjiang Xingyang Industry & Trade Co.,Ltd. , https://www.xycaster.com