RFID is gradually merging with sensor technology. The combination of sensor technology and RFID technology will create a ubiquitous, sensory network that is perceived by people at any time. This brings a new dimension to the management of medical supplies, especially blood management. Opportunity. As one of the major manufacturing and consumer countries, China should firmly seize this opportunity to promote the development of the local RFID industry and improve the level of social information.
The Feasibility of RFID Fusion Sensing Technology for Blood Management
The general process of the blood management business is: blood donation registration, one blood test, one blood test, one blood bank, one inventory management (component treatment, etc.), one blood delivery, and one hospital for patients (or other blood products). In this process, a large amount of data information is often involved, including blood donor's data, blood type, blood collection time, location, handling person, etc. A lot of information brings certain difficulties to the management of the blood. Plus, blood is a substance that is very easy to degenerate. If the environmental conditions are not suitable, the quality of the blood is destroyed, so the blood is stored and transported in a quality manner. Real-time monitoring is also critical. RFID and sensing technology are emerging technologies that can solve the above problems and effectively help blood management.
RFID technology can provide each bag blood with its own unique identity and store its corresponding information. This information is interconnected with the back-end database. Therefore, the blood is at the blood collection point, the transfer point blood bank, or the point-of-use hospital. All of them can be monitored by the RFID system. The information of the blood at each mobilization point can be tracked at any time. Previous blood deposits are time-consuming and labor-intensive, and manual verification of information is required before use. With RFID technology, data can be collected, transmitted, checked, and updated in real time without the need for precise positioning, accelerating the emergence of blood. Library identification also avoids manual errors that often occur. The RFID's non-contact recognition feature also ensures that the blood will be identified and detected under conditions that will not be contaminated, reducing the possibility of blood contamination, it is not afraid of dust, stains, low temperature, etc., can store special blood Maintain normal working conditions under environmental conditions.
Sensing technology is a window for sensing, acquiring and detecting information. It can realize data collection and quantification, processing fusion and transmission applications. Through the sensor's real-time monitoring and collection of the blood environment temperature, sealing conditions and oscillation level, and then through the system's timely processing and response to the sensed information, it can effectively prevent blood from deteriorating and ensure the quality of blood.
Integrate RFID and sensor technology, and use RFID sensor tags that can improve the recognition efficiency, achieve information tracking, and can monitor the quality of articles in real time, and can truly realize the intelligent information management of blood management.
RFID sensor tag design
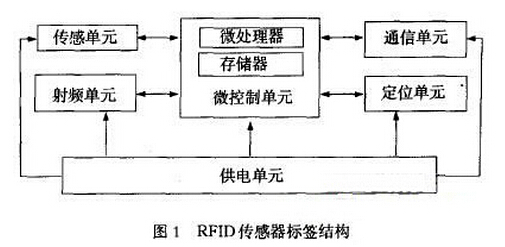
The RFID sensor tag is mainly composed of a micro control unit, a sensing unit, a radio frequency unit, a communication unit, a positioning unit, and a power supply unit, as shown in FIG. 1 .

1. Micro-control unit The micro-control unit consists of an embedded system, including an embedded microprocessor, memory, embedded operating system, etc. It also integrates a watchdog, timer/counter, synchronous/asynchronous serial interface, and A. Various necessary functions and external devices such as /D and D/A converters and I/O. The main functions implemented by the unit include: responsible for the task allocation and scheduling of the entire chip, data integration and transmission, wireless data verification, data analysis, storage and forwarding, routing maintenance of the intra-area network, and power management of the chip power supply. Wait.
2. The sensing unit The sensing unit is mainly composed of sensors and A/D converters. A sensor is a device or device that can sense a specified measurement and convert it into a usable output signal according to a certain law. Usually, the sensor is composed of a sensitive element and a conversion element. The sensitive element collects information that needs to be sensed externally and sends it to the conversion element. The latter converts the above physical quantity into an original electric signal that the system can recognize, and passes the integration circuit and amplifying circuit. The shaping process is finally converted into a digital signal by A/D and sent to the micro-control unit for further processing.
Taking into account the requirements of environmental conditions for blood storage and transportation, the sensing unit includes functions for testing physical signals such as temperature, pressure, light sensitivity, and oscillation in the monitoring area.
3, RF unit RF control unit to receive and send RF signals, and choose to use space multiplexing, time division multiplexing, frequency division multiplexing and code division multiple access methods to achieve multi-target simultaneous recognition and system anti-collision mechanism.
4. Communication unit The communication unit is used for data communication to solve the carrier frequency band selection, data transmission rate, signal modulation, coding method, etc. in the wireless communication, and transmits and receives data between the chip and the reader/writer through the antenna, and has data fusion. Requests for arbitration and routing.
5. The positioning unit positioning unit realizes the positioning of the chip's own position and the positioning of the information transmission position. Based on wireless transmission protocols such as IEEE802.15.4 standard and ZigBee protocol. The positioning algorithm can be selected based on ranging (such as signal strength ranging, time difference ranging, etc.) or not based on ranging (such as centroid method, DV-Hop algorithm, etc.).
6, power supply unit RFID sensor tag passive, semi-passive and active points. Passive tags do not require a built-in battery. It maintains its work by extracting the RF energy emitted by the reader. Both semi-passive and active tags require internal battery power to maintain normal sensing and RF operation. Considering that the real-time monitoring of blood products in blood management needs to ensure its continuous and normal energy supply, the power supply unit is added and designed as a semi-passive or active label [4].
In this section, by properly setting the receiving, transmitting, and standby states of the chip, the problem of energy consumption and transmission reliability can be solved, and the useful life of the chip can be effectively extended.
Application of RFID Sensor Tag in Blood Management
Mainly from the three aspects of blood out of storage management, blood tracking management, and blood quality control management, pointing out the effective role of RFID fusion sensing technology in blood management.
1. Blood storage and storage management (1) Blood storage workers transfer the blood bags to the population of the conveyor belt in turn. The bottom of the conveyor belt is equipped with an RFID reader. When the RFID sensor label attached to the blood bag is read and read In the range, the information on the label is read out, filtered by the middleware and transmitted to the back-end database. At the same time, the system displays the blood type, type, specification and other information on the screen at the outlet of the conveyor belt. The staff according to the displayed content, the blood Respectively put into the designated storage tray.
According to the blood type, type, specification, quantity, etc. read out, the back-end system carries out the identification of the location in the blood bank to find the existing empty space that meets the specifications and quantity. This step is mainly achieved by pasting an RFID tag on each shelf and writing information on the type, type, specification, quantity, etc. of the blood to be stored by the reader. When a blood bag is placed on the shelf At the time, the worker uses a handheld reader/writer to set and write the RFID tag. When the blood bag on the shelf is out of storage or is displaced, the worker uses a handheld reader/writer to write and write the RFID tag. The reader mounted on the top of the blood bank will read the shelf labels when instructed by the system, and will find that the shelves that have been cleared and meet the storage conditions inform the system, and the system will put the shelf The specific number is displayed on the screen at the warehouse, telling staff which types of blood should be placed on which shelves.
When the staff is instructed, the blood of various specifications will be sent to the designated area for refrigerated storage. At the same time, the reader/writer writes information such as the time of storage of the blood bags, the type of warehousing, blood donors, and blood recipients into the RFID system.
(2) The blood delivery system issues a shipping order to instruct the staff to take out blood of the specified type, specification and quantity to the designated area. If the amount of blood taken is small, the staff can use a handheld reader to read the blood information directly; if the amount of blood taken is large, the staff can use the belt to transport the blood out of the warehouse and read its information. The information read out is transmitted to the system and checked against the back-end database. If it is correct, it is allowed to be released. During the outbound process, the RFID system records the time of delivery, blood expiration date, and other minor information.
The sequence of blood withdrawal is decided after the system reads the information and requires that the blood of the same specification be in accordance with the principle of first-in, first-out, to avoid the phenomenon of inventory backlog and waste of blood. Blood is forbidden to be released from the blood bank in the state marked as "to be tested" to ensure the quality of the blood released.
2. Blood tracking management Blood tracking management uses a cluster-based hierarchical structure. Each cluster head is a distributed information processing center. It is used to collect the data of each cluster member and complete the data processing and fusion. Then the data is transmitted to the cluster head of the next layer and passed in sequence. Finally, all the data are filtered and After the integration, it is transmitted to the top of the cluster head, and the reverse process is the information query process. The data is developed layer by layer and tracked in an orderly manner. Here, the highest level of cluster heads is equivalent to the nation's blood information center, while the second highest level of cluster heads is equivalent to the blood information centers of provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities, and so on. The lowest level of cluster members is each grassroots blood station. This layered structure spreads information, avoids centralized storage, solves the problem of excessive information volume, and improves the security of the system. Information exchange and delivery are directly expanded between the sub-layer and the parent layer, facilitating the query and tracking.
The process of storing blood information is: First, store the RFID identification code of each bag of blood and its corresponding information in the database of the primary blood bank, and then merge the information of the primary blood station, and the identification code and the effective IP of the primary blood station. The address is stored in the local city-level blood information center database, and then the information of the city-level blood information center is integrated, and the identification code and the effective IP address of the municipal blood information center are stored in the local provincial-level blood information center database. Reintegrate the information from the provincial blood information center and save the identification code and the effective IP address of the provincial blood information center to the National Blood Information Center database (if necessary, you can also add the identification code to the country's blood information center The effective IP address is stored in the global blood information center database for global blood information interconnection.)
The blood information tracking process is as follows: According to the RFID identification code, it firstly searches the National Blood Information Center database for the province's information about the blood of the bag, and then goes to the provincial blood information center database to find the blood of the bag according to the IP address it finds. City information, based on the found IP address, enters the city-level blood information center database to find the blood station to which the blood belongs, and enters the blood bank database according to the found IP address, according to which information the current blood of the bag can be known. Whether the status is stored in the library or used out of the library or has been corrupted, if it is already used, you can further find the user's full information.
3, blood quality control management Blood is very sensitive to changes in temperature, if the ambient temperature is not appropriate, the material in the blood is destroyed, which will affect the quality of the blood and shelf life. In the process of storage, delivery, and transportation, blood should also avoid violent oscillations. In addition, the packaging of blood should be sealed. If bacterial contamination occurs due to puncture or other factors, the blood will be scrapped.
The RFID sensor tag affixed on the blood bag will monitor the environment surrounding the blood bag in real time, and measure the surrounding physical signals such as temperature, pressure, sensation, and oscillation at regular time intervals, and record the measurement data in the tag chip. . The system will set a standard range inside the tag. Once the current measured data is lower than the lower limit of the range or the upper limit of the range, the tag will automatically send a radio frequency signal to activate the alarm device to prompt the staff.
If the blood bag is alarmed in the blood bank storage state, according to the received RF signal, the current position of the alarm blood bag (reservoir area, shelf, RFID identification code, etc.) will be displayed on the alarm display screen, so that the staff can promptly discover and Processing; If the blood bag is in the middle of transportation, the alarm device can be installed on the transport storage, prompting the staff with howling or flashing. After the staff discovers, the radio frequency signal is received by the handheld reader and the alarm is found according to the identification code. Blood bag.
Once the blood is suspected of being degraded or contaminated, the worker will use the reader to set the label to the "to be tested" status, not allowed to leave the library, the use of the point is not allowed to use, after the test is confirmed to have been unable to use The high-pressure disinfection and incineration treatment will be performed. At this time, the staff will write scrap information and scrap reasons to the system for the RFID identification code of the bagged blood, so as to prepare for the follow-up blood tracking.
For the returned blood, in addition to the need to manually detect the blood quality, it is also possible to find out the problems in the whole process from blood collection to blood supply to blood withdrawal through the data recording of RFID sensor tags, and to find out the responsibility for the problem. The person or organization analyzes the reason to avoid the next occurrence of a similar situation.
Blood is both a source of life and a source of transmission of many diseases. Common diseases transmitted through blood transfusion or blood products include: hepatitis B, hepatitis C, AIDS, syphilis, malaria, and sepsis, most of which are difficult to cure. In order to avoid disease infections or medical accidents caused by irregular blood collection, bagged blood management disorders or improper blood transfusions, it is imperative to strengthen blood management and ensure blood safety. At present, the combination of RFID and sensor technology is not very extensive, but it has shown a broad application prospects. This paper proposes an RFID sensor tag designed by combining these two technologies and analyzes the advantages and feasibility of applying it to blood management.
Blood management is a work that does not allow mistakes. The use of RFID sensor tags in these applications not only makes the entire supply chain management visible, transparent, and free from contamination, but also enables real-time monitoring and interconnection of information, quality, etc. The informationization of management informatization and medical management has extended to the periphery and fell into place, so that fully individualized humanistic care has been realized.
Aluminium die cast die is a manufacturing process that involves the production of communication accessories Aluminium die casting using aluminium as the primary material. This process is widely used in the telecommunications industry to create high-quality and durable products.
The Feasibility of RFID Fusion Sensing Technology for Blood Management
The general process of the blood management business is: blood donation registration, one blood test, one blood test, one blood bank, one inventory management (component treatment, etc.), one blood delivery, and one hospital for patients (or other blood products). In this process, a large amount of data information is often involved, including blood donor's data, blood type, blood collection time, location, handling person, etc. A lot of information brings certain difficulties to the management of the blood. Plus, blood is a substance that is very easy to degenerate. If the environmental conditions are not suitable, the quality of the blood is destroyed, so the blood is stored and transported in a quality manner. Real-time monitoring is also critical. RFID and sensing technology are emerging technologies that can solve the above problems and effectively help blood management.
RFID technology can provide each bag blood with its own unique identity and store its corresponding information. This information is interconnected with the back-end database. Therefore, the blood is at the blood collection point, the transfer point blood bank, or the point-of-use hospital. All of them can be monitored by the RFID system. The information of the blood at each mobilization point can be tracked at any time. Previous blood deposits are time-consuming and labor-intensive, and manual verification of information is required before use. With RFID technology, data can be collected, transmitted, checked, and updated in real time without the need for precise positioning, accelerating the emergence of blood. Library identification also avoids manual errors that often occur. The RFID's non-contact recognition feature also ensures that the blood will be identified and detected under conditions that will not be contaminated, reducing the possibility of blood contamination, it is not afraid of dust, stains, low temperature, etc., can store special blood Maintain normal working conditions under environmental conditions.
Sensing technology is a window for sensing, acquiring and detecting information. It can realize data collection and quantification, processing fusion and transmission applications. Through the sensor's real-time monitoring and collection of the blood environment temperature, sealing conditions and oscillation level, and then through the system's timely processing and response to the sensed information, it can effectively prevent blood from deteriorating and ensure the quality of blood.
Integrate RFID and sensor technology, and use RFID sensor tags that can improve the recognition efficiency, achieve information tracking, and can monitor the quality of articles in real time, and can truly realize the intelligent information management of blood management.
RFID sensor tag design
The RFID sensor tag is mainly composed of a micro control unit, a sensing unit, a radio frequency unit, a communication unit, a positioning unit, and a power supply unit, as shown in FIG. 1 .

1. Micro-control unit The micro-control unit consists of an embedded system, including an embedded microprocessor, memory, embedded operating system, etc. It also integrates a watchdog, timer/counter, synchronous/asynchronous serial interface, and A. Various necessary functions and external devices such as /D and D/A converters and I/O. The main functions implemented by the unit include: responsible for the task allocation and scheduling of the entire chip, data integration and transmission, wireless data verification, data analysis, storage and forwarding, routing maintenance of the intra-area network, and power management of the chip power supply. Wait.
2. The sensing unit The sensing unit is mainly composed of sensors and A/D converters. A sensor is a device or device that can sense a specified measurement and convert it into a usable output signal according to a certain law. Usually, the sensor is composed of a sensitive element and a conversion element. The sensitive element collects information that needs to be sensed externally and sends it to the conversion element. The latter converts the above physical quantity into an original electric signal that the system can recognize, and passes the integration circuit and amplifying circuit. The shaping process is finally converted into a digital signal by A/D and sent to the micro-control unit for further processing.
Taking into account the requirements of environmental conditions for blood storage and transportation, the sensing unit includes functions for testing physical signals such as temperature, pressure, light sensitivity, and oscillation in the monitoring area.
3, RF unit RF control unit to receive and send RF signals, and choose to use space multiplexing, time division multiplexing, frequency division multiplexing and code division multiple access methods to achieve multi-target simultaneous recognition and system anti-collision mechanism.
4. Communication unit The communication unit is used for data communication to solve the carrier frequency band selection, data transmission rate, signal modulation, coding method, etc. in the wireless communication, and transmits and receives data between the chip and the reader/writer through the antenna, and has data fusion. Requests for arbitration and routing.
5. The positioning unit positioning unit realizes the positioning of the chip's own position and the positioning of the information transmission position. Based on wireless transmission protocols such as IEEE802.15.4 standard and ZigBee protocol. The positioning algorithm can be selected based on ranging (such as signal strength ranging, time difference ranging, etc.) or not based on ranging (such as centroid method, DV-Hop algorithm, etc.).
6, power supply unit RFID sensor tag passive, semi-passive and active points. Passive tags do not require a built-in battery. It maintains its work by extracting the RF energy emitted by the reader. Both semi-passive and active tags require internal battery power to maintain normal sensing and RF operation. Considering that the real-time monitoring of blood products in blood management needs to ensure its continuous and normal energy supply, the power supply unit is added and designed as a semi-passive or active label [4].
In this section, by properly setting the receiving, transmitting, and standby states of the chip, the problem of energy consumption and transmission reliability can be solved, and the useful life of the chip can be effectively extended.
Application of RFID Sensor Tag in Blood Management
Mainly from the three aspects of blood out of storage management, blood tracking management, and blood quality control management, pointing out the effective role of RFID fusion sensing technology in blood management.
1. Blood storage and storage management (1) Blood storage workers transfer the blood bags to the population of the conveyor belt in turn. The bottom of the conveyor belt is equipped with an RFID reader. When the RFID sensor label attached to the blood bag is read and read In the range, the information on the label is read out, filtered by the middleware and transmitted to the back-end database. At the same time, the system displays the blood type, type, specification and other information on the screen at the outlet of the conveyor belt. The staff according to the displayed content, the blood Respectively put into the designated storage tray.
According to the blood type, type, specification, quantity, etc. read out, the back-end system carries out the identification of the location in the blood bank to find the existing empty space that meets the specifications and quantity. This step is mainly achieved by pasting an RFID tag on each shelf and writing information on the type, type, specification, quantity, etc. of the blood to be stored by the reader. When a blood bag is placed on the shelf At the time, the worker uses a handheld reader/writer to set and write the RFID tag. When the blood bag on the shelf is out of storage or is displaced, the worker uses a handheld reader/writer to write and write the RFID tag. The reader mounted on the top of the blood bank will read the shelf labels when instructed by the system, and will find that the shelves that have been cleared and meet the storage conditions inform the system, and the system will put the shelf The specific number is displayed on the screen at the warehouse, telling staff which types of blood should be placed on which shelves.
When the staff is instructed, the blood of various specifications will be sent to the designated area for refrigerated storage. At the same time, the reader/writer writes information such as the time of storage of the blood bags, the type of warehousing, blood donors, and blood recipients into the RFID system.
(2) The blood delivery system issues a shipping order to instruct the staff to take out blood of the specified type, specification and quantity to the designated area. If the amount of blood taken is small, the staff can use a handheld reader to read the blood information directly; if the amount of blood taken is large, the staff can use the belt to transport the blood out of the warehouse and read its information. The information read out is transmitted to the system and checked against the back-end database. If it is correct, it is allowed to be released. During the outbound process, the RFID system records the time of delivery, blood expiration date, and other minor information.
The sequence of blood withdrawal is decided after the system reads the information and requires that the blood of the same specification be in accordance with the principle of first-in, first-out, to avoid the phenomenon of inventory backlog and waste of blood. Blood is forbidden to be released from the blood bank in the state marked as "to be tested" to ensure the quality of the blood released.
2. Blood tracking management Blood tracking management uses a cluster-based hierarchical structure. Each cluster head is a distributed information processing center. It is used to collect the data of each cluster member and complete the data processing and fusion. Then the data is transmitted to the cluster head of the next layer and passed in sequence. Finally, all the data are filtered and After the integration, it is transmitted to the top of the cluster head, and the reverse process is the information query process. The data is developed layer by layer and tracked in an orderly manner. Here, the highest level of cluster heads is equivalent to the nation's blood information center, while the second highest level of cluster heads is equivalent to the blood information centers of provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities, and so on. The lowest level of cluster members is each grassroots blood station. This layered structure spreads information, avoids centralized storage, solves the problem of excessive information volume, and improves the security of the system. Information exchange and delivery are directly expanded between the sub-layer and the parent layer, facilitating the query and tracking.
The process of storing blood information is: First, store the RFID identification code of each bag of blood and its corresponding information in the database of the primary blood bank, and then merge the information of the primary blood station, and the identification code and the effective IP of the primary blood station. The address is stored in the local city-level blood information center database, and then the information of the city-level blood information center is integrated, and the identification code and the effective IP address of the municipal blood information center are stored in the local provincial-level blood information center database. Reintegrate the information from the provincial blood information center and save the identification code and the effective IP address of the provincial blood information center to the National Blood Information Center database (if necessary, you can also add the identification code to the country's blood information center The effective IP address is stored in the global blood information center database for global blood information interconnection.)
The blood information tracking process is as follows: According to the RFID identification code, it firstly searches the National Blood Information Center database for the province's information about the blood of the bag, and then goes to the provincial blood information center database to find the blood of the bag according to the IP address it finds. City information, based on the found IP address, enters the city-level blood information center database to find the blood station to which the blood belongs, and enters the blood bank database according to the found IP address, according to which information the current blood of the bag can be known. Whether the status is stored in the library or used out of the library or has been corrupted, if it is already used, you can further find the user's full information.
3, blood quality control management Blood is very sensitive to changes in temperature, if the ambient temperature is not appropriate, the material in the blood is destroyed, which will affect the quality of the blood and shelf life. In the process of storage, delivery, and transportation, blood should also avoid violent oscillations. In addition, the packaging of blood should be sealed. If bacterial contamination occurs due to puncture or other factors, the blood will be scrapped.

The RFID sensor tag affixed on the blood bag will monitor the environment surrounding the blood bag in real time, and measure the surrounding physical signals such as temperature, pressure, sensation, and oscillation at regular time intervals, and record the measurement data in the tag chip. . The system will set a standard range inside the tag. Once the current measured data is lower than the lower limit of the range or the upper limit of the range, the tag will automatically send a radio frequency signal to activate the alarm device to prompt the staff.
If the blood bag is alarmed in the blood bank storage state, according to the received RF signal, the current position of the alarm blood bag (reservoir area, shelf, RFID identification code, etc.) will be displayed on the alarm display screen, so that the staff can promptly discover and Processing; If the blood bag is in the middle of transportation, the alarm device can be installed on the transport storage, prompting the staff with howling or flashing. After the staff discovers, the radio frequency signal is received by the handheld reader and the alarm is found according to the identification code. Blood bag.
Once the blood is suspected of being degraded or contaminated, the worker will use the reader to set the label to the "to be tested" status, not allowed to leave the library, the use of the point is not allowed to use, after the test is confirmed to have been unable to use The high-pressure disinfection and incineration treatment will be performed. At this time, the staff will write scrap information and scrap reasons to the system for the RFID identification code of the bagged blood, so as to prepare for the follow-up blood tracking.
For the returned blood, in addition to the need to manually detect the blood quality, it is also possible to find out the problems in the whole process from blood collection to blood supply to blood withdrawal through the data recording of RFID sensor tags, and to find out the responsibility for the problem. The person or organization analyzes the reason to avoid the next occurrence of a similar situation.
Blood is both a source of life and a source of transmission of many diseases. Common diseases transmitted through blood transfusion or blood products include: hepatitis B, hepatitis C, AIDS, syphilis, malaria, and sepsis, most of which are difficult to cure. In order to avoid disease infections or medical accidents caused by irregular blood collection, bagged blood management disorders or improper blood transfusions, it is imperative to strengthen blood management and ensure blood safety. At present, the combination of RFID and sensor technology is not very extensive, but it has shown a broad application prospects. This paper proposes an RFID sensor tag designed by combining these two technologies and analyzes the advantages and feasibility of applying it to blood management.
Blood management is a work that does not allow mistakes. The use of RFID sensor tags in these applications not only makes the entire supply chain management visible, transparent, and free from contamination, but also enables real-time monitoring and interconnection of information, quality, etc. The informationization of management informatization and medical management has extended to the periphery and fell into place, so that fully individualized humanistic care has been realized.
communication accessories Aluminium die casting
Aluminium die cast die is a manufacturing process that involves the production of communication accessories Aluminium die casting using aluminium as the primary material. This process is widely used in the telecommunications industry to create high-quality and durable products.
During the aluminum metal casting process, molten aluminium is injected into a die or mold under high pressure. The aluminium solidifies quickly, taking the shape of the mold and creating a precise and detailed communication accessory. This process allows for the production of intricate designs with excellent dimensional accuracy.
die cast die,aluminum metal casting,communication accessories Aluminium die casting
Shenzhen Kangneng Fusheng Die Casting Products Co., Ltd. , https://www.knfsdiecasting.com